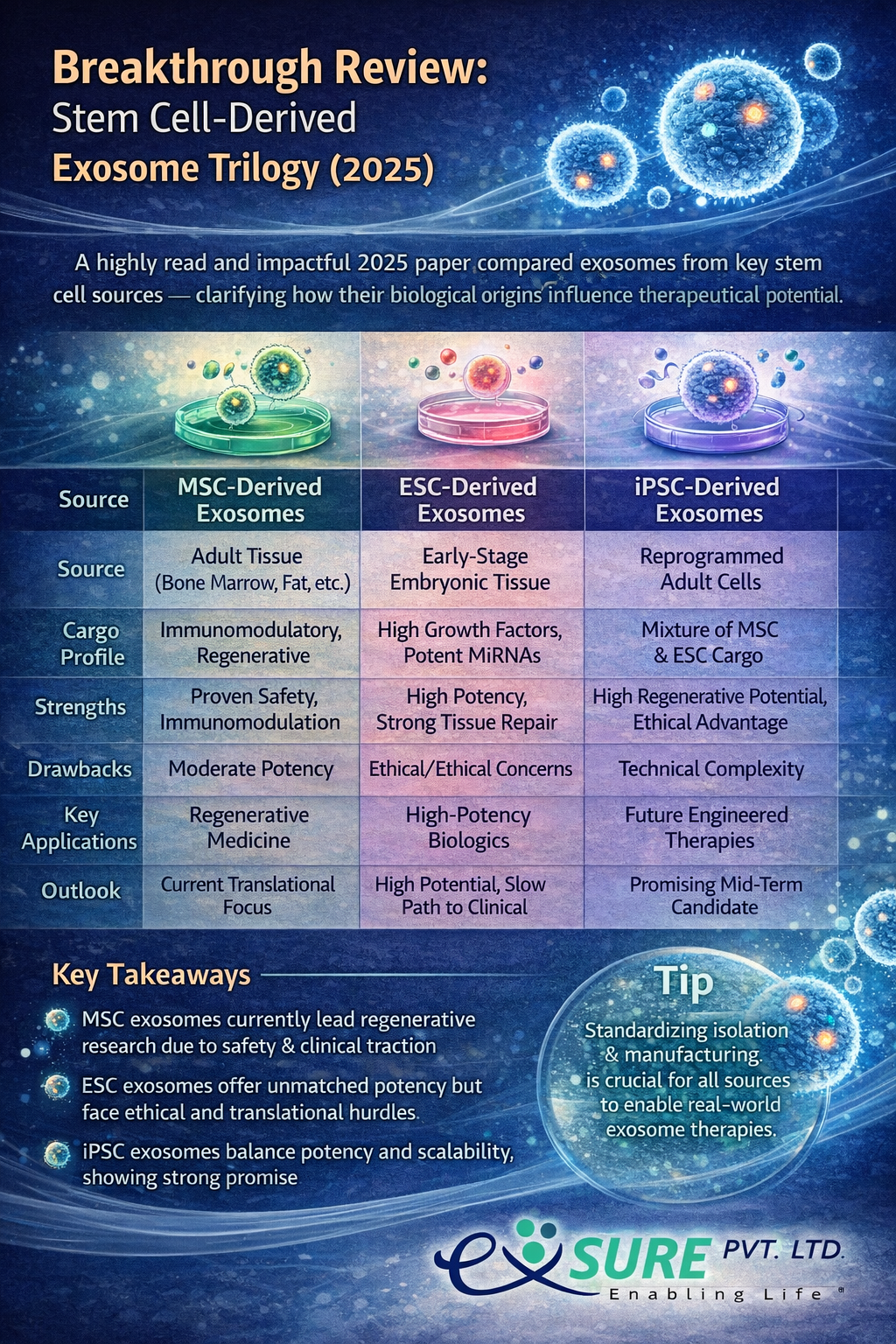
In 2025, one of the most read and impactful exosome research papers—“Stem cell derived exosome trilogy: an epic comparison of human MSCs, ESCs and iPSCs”—synthesized global insights into exosome biology and therapeutic potential. By comparing exosomes from three major stem cell types, the review clarifies how biological origin influences cargo composition, therapeutic utility, and translational readiness.
Key insights include:
- MSC-derived exosomes currently dominate translational research due to their robust immunomodulatory and regenerative cargo.
- ESC-derived exosomes showcase high biological potency but face practical and ethical challenges.
- iPSC-derived exosomes offer a promising balance of potency and scalability, potentially accelerating clinical adoption.
This comparative framework helps developers and investors understand where the field is heading and highlights why standardization of isolation, characterization, and manufacturing is crucial for moving exosome therapeutics out of the lab and into clinical use.
1. Exosomes Are Transitioning from Experimental Tools to Therapeutic Platforms
The field has moved beyond basic discovery. Exosomes are now being developed as:
- Regenerative therapeutics
- Targeted drug delivery vehicles
- Immune modulators
- Diagnostic biomarkers
The review emphasizes that clinical translation is accelerating, particularly in dermatology, orthopedics, neurology, and wound healing.
2. Mechanism of Action Is Now Better Defined
Exosomes function through:
- miRNA and mRNA cargo delivery
- Growth factors and cytokine signaling
- Immunomodulatory effects
- Angiogenesis stimulation
- Anti-inflammatory pathways
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes remain the most studied due to their strong regenerative and anti-inflammatory properties.
3. Manufacturing Scalability Is Critical
To achieve commercial viability:
- GMP-compliant production systems are essential
- Bioreactor-based MSC expansion is preferred
- Closed-system purification improves consistency
- Batch-to-batch reproducibility must be validated
Scalable manufacturing remains one of the main translational challenges.
References:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s13287-025-04440-0
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/nanotechnology/articles/10.3389/fnano.2022.939197/full



